Delegated User Authentication¶
This guide covers OAuth2 flows that involve user interaction and consent, allowing applications to access HouMeerOver data on behalf of users. This approach provides enhanced security and user control over data access.
What is Delegated Authentication?¶
Delegated authentication allows applications to access APIs on behalf of users, with explicit user consent. Unlike server-to-server authentication, delegated flows require user interaction and provide:
- User consent for data access
- User-scoped permissions instead of application-wide access
- Enhanced security through user authorization
- Revocable access controlled by the user
User-Controlled Access Advantages¶
✅ Enhanced Security:
- Users explicitly authorize data access
- Applications receive limited, user-specific permissions
- Users can revoke access at any time
- Audit trail of user authorization events
✅ Compliance Benefits:
- Meets privacy regulation requirements
- Clear consent mechanisms
- User data ownership respect
- Transparent data usage
✅ Flexible Integration:
- Supports various application types
- Enables third-party integrations
- Allows user-specific features
- Supports multi-tenant scenarios
Supported Delegated Grant Types¶
HouMeerOver supports several OAuth2 grant types for different application scenarios:
Authorization Code Flow (PKCE)¶
Primary Choice for Modern Applications
- Use Case: Web applications, mobile apps, SPAs
- Security: Highest security with PKCE extension
- User Experience: Secure redirect-based authorization
- OIDC Support: Yes, with optional OpenID Connect
✅ Best for: Web applications, mobile apps, secure SPAs
Implicit Flow¶
Legacy Support for Client-Side Applications
- Use Case: Single-page applications (SPAs)
- Security: Lower security, tokens in URL fragments
- User Experience: Direct token return
- OIDC Support: Yes, with optional OpenID Connect
⚠️ Note: Deprecated in favor of Authorization Code + PKCE
OpenID Connect Hybrid Flow¶
Complex Identity Scenarios
- Use Case: Applications requiring both ID tokens and access tokens
- Security: High security with multiple token types
- User Experience: Rich identity information
- OIDC Support: Full OpenID Connect implementation
✅ Best for: Enterprise applications with complex identity needs
Authorization Code Flow Implementation¶
The Authorization Code flow is the most secure OAuth2 flow for delegated authentication. Follow these step-by-step instructions to implement it in your application.
Step 1: Register Your Application¶
1.1 Access Application Registration¶
- Log into the HouMeerOver administration interface
- Navigate to Third Party Applications → OAuth2 Applications
- Click Add OAuth2 Application
1.2 Configure Application Details¶
Fill out the application registration form:
Basic Information:
- Name: Descriptive name (e.g., "Municipal Web Portal")
- Client Type: Select "Confidential" for web apps or "Public" for SPAs/mobile apps
- Authorization Grant Type: Select "Authorization code"
Redirect URIs: Add all valid callback URLs for your application:
https://yourapp.com/oauth/callback
http://localhost:3000/oauth/callback (for development)
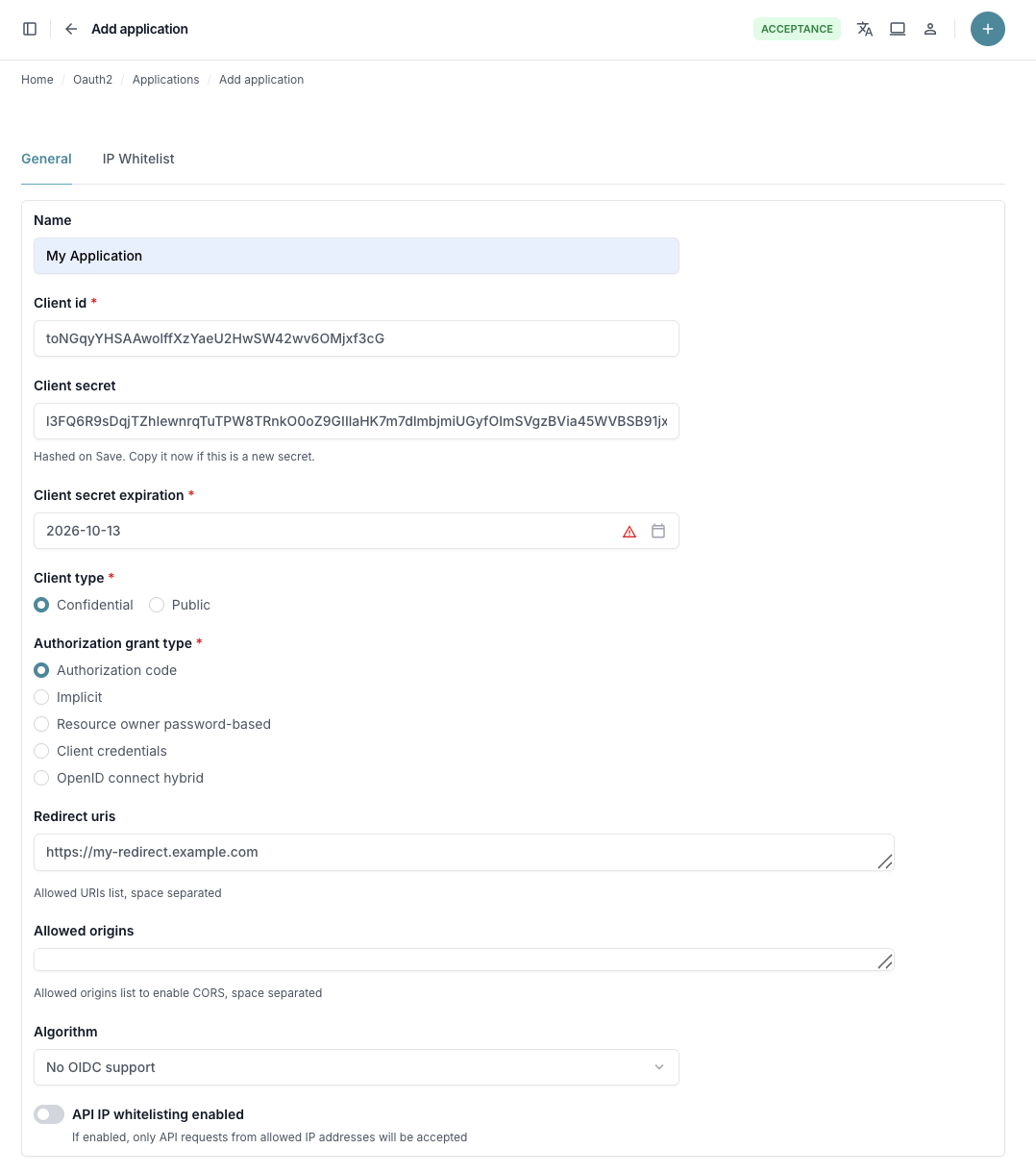
IP Whitelisting (Optional):
- Enable and add IP addresses that should be allowed to use this application
- Leave disabled to allow access from any IP address
- Recommended for production environments for additional security
1.3 Save Application and Get Credentials¶
- Important: Copy your
Client IDandClient Secretbefore saving (the client secret will be hashed after saving) - Click Save to create the application
- Note these endpoints:
- Authorization URL:
https://api.houmeerover.nl/o/authorize/ - Token URL:
https://api.houmeerover.nl/o/token/
- Authorization URL:
Step 2: Generate PKCE Parameters¶
For security, generate PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) parameters:
import random
import string
import base64
import hashlib
# Generate code_verifier (43-128 characters)
code_verifier = ''.join(random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits)
for _ in range(random.randint(43, 128)))
# Generate code_challenge
code_challenge = hashlib.sha256(code_verifier.encode('utf-8')).digest()
code_challenge = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(code_challenge).decode('utf-8').replace('=', '')
print(f"Code Verifier: {code_verifier}")
print(f"Code Challenge: {code_challenge}")
Store the code_verifier securely - you'll need it in step 4.
Step 3: Redirect User for Authorization¶
3.1 Build Authorization URL¶
Create the authorization URL with required parameters:
https://api.houmeerover.nl/o/authorize/?response_type=code&code_challenge=YOUR_CODE_CHALLENGE&code_challenge_method=S256&client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URI
Required Parameters:
response_type=codeclient_id: Your application's client IDredirect_uri: Must match registered URI exactlycode_challenge: Generated PKCE challengecode_challenge_method=S256
Optional Parameters:
state: Random string to prevent CSRF attacks (recommended)scope: Requested permissions (e.g.,read write)
3.2 Redirect User¶
Direct the user to this URL in their browser. They will:
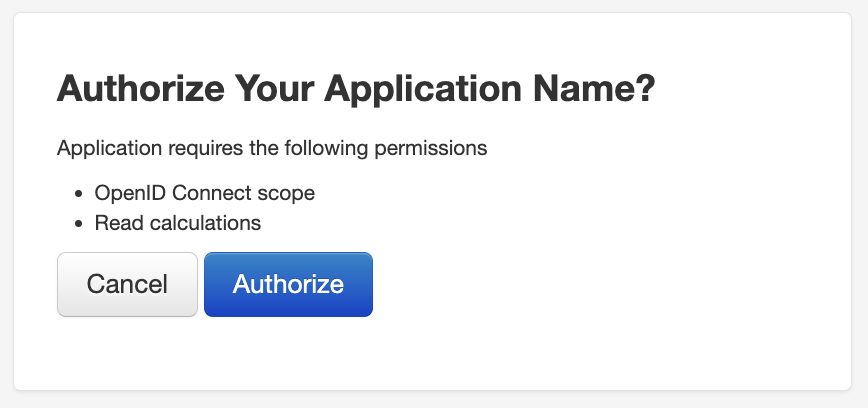
- See HouMeerOver login page (if not already logged in)
- See authorization consent screen
- Be redirected back to your
redirect_uriwith authorization code
Step 4: Handle Authorization Response¶
4.1 Parse Callback¶
After user authorization, HouMeerOver redirects to your callback URL:
https://yourapp.com/oauth/callback?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE
Extract the authorization code from the URL parameters.
4.2 Exchange Code for Access Token¶
Make a POST request to exchange the authorization code for an access token:
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
"https://api.houmeerover.nl/o/token/" \
-d "client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID" \
-d "client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET" \
-d "code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE" \
-d "code_verifier=YOUR_CODE_VERIFIER" \
-d "redirect_uri=YOUR_REDIRECT_URI" \
-d "grant_type=authorization_code"
Required Parameters:
- client_id: Your application's client ID
- client_secret: Your application's client secret (for confidential clients)
- code: Authorization code from callback
- code_verifier: The verifier used to generate code_challenge
- redirect_uri: Same URI used in authorization request
- grant_type=authorization_code
4.3 Parse Token Response¶
Successful response contains access token:
{
"access_token": "jooqrnOrNa0BrNWlg68u9sl6SkdFZg",
"expires_in": 36000,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"scope": "read write",
"refresh_token": "HNvDQjjsnvDySaK0miwG4lttJEl9yD"
}
Step 5: Use Access Token for API Calls¶
Include the access token in API requests:
curl \
-H "Authorization: Bearer jooqrnOrNa0BrNWlg68u9sl6SkdFZg" \
-X GET https://api.houmeerover.nl/api/v1/calculations/
Step 6: Use Refresh Token¶
When access tokens expire (after 10 hours), use the refresh token to get a new access token without requiring user re-authentication.
6.1 Refresh Access Token¶
Make a POST request with your refresh token:
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
"https://api.houmeerover.nl/o/token/" \
-d "grant_type=refresh_token" \
-d "refresh_token=YOUR_REFRESH_TOKEN" \
-d "client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID" \
-d "client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET"
Required Parameters:
- grant_type=refresh_token
- refresh_token: The refresh token from step 4.3
- client_id: Your application's client ID
- client_secret: Your application's client secret (for confidential clients)
6.2 Parse Refresh Response¶
Successful response contains new tokens:
{
"access_token": "new_access_token_here",
"expires_in": 36000,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"scope": "read write",
"refresh_token": "new_refresh_token_here"
}
Important Notes: - Store the new access token and refresh token - The old refresh token may be invalidated (depending on server configuration) - Implement automatic token refresh in your application when API calls return 401 errors
Security Best Practices¶
PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange)¶
Always Use PKCE:
- Required for public clients (SPAs, mobile apps)
- Recommended for confidential clients
- Prevents authorization code interception attacks
- Use
code_challenge_method=S256(SHA256)
Client Credentials Protection¶
Confidential Applications:
- Store client secrets in environment variables
- Never expose secrets in client-side code
- Use secure server-side storage only
- Rotate secrets every 90 days
Public Applications:
- No client secret - rely on PKCE and redirect URI validation
- Register all authorized redirect URIs exactly
- Use HTTPS redirect URIs in production
State Parameter Validation¶
CSRF Protection:
- Always include
stateparameter in authorization requests - Generate cryptographically secure random state values
- Store state securely during the flow
- Always verify state parameter matches in callback
Token Security¶
Access Token Handling:
- Store tokens securely (HttpOnly cookies for web apps)
- Never log access tokens in application logs
- Implement automatic token refresh when available
- Access tokens expire after 10 hours (36000 seconds)
Token Storage:
- Web apps: Use secure HTTP-only cookies
- SPAs: Use memory storage, not localStorage
- Mobile: Use secure keychain/keystore
IP Whitelisting¶
When to Use:
- Enable IP whitelisting for production applications
- Add your server's static IP addresses during application setup
- Provides an additional security layer beyond client credentials
Configuration:
- Enable IP whitelisting in the OAuth2 application settings
- Add IP addresses in the IP Whitelist tab
- Specify IP address to whitelist (e.g.,
192.168.1.1) - Use CIDR notation for IP ranges (e.g.,
192.168.1.0/24) - Leave off only for development environments
Troubleshooting¶
Common Issues¶
1. Redirect URI Mismatch¶
Error: redirect_uri_mismatch
Solutions:
- Verify exact redirect URI is registered in application settings
- Ensure exact match: protocol, domain, path, no trailing slash differences
- Add all required URIs (development, staging, production)
2. PKCE Validation Errors¶
Error: invalid_request (PKCE-related)
Solutions:
- Ensure
code_challengeis SHA256 hash, base64url-encoded - Use
code_challenge_method=S256 - Store and reuse the same
code_verifierfrom step 2 - Verify base64url encoding (not standard base64)
3. Authorization Code Issues¶
Error: invalid_grant or authorization_code_expired
Solutions:
- Complete token exchange within 10 minutes of authorization
- Don't reuse authorization codes (they're single-use)
- Use exact same
redirect_uriin token request as authorization request
4. Client Authentication Failures¶
Error: invalid_client
Solutions:
- Verify
client_idandclient_secretare correct - Check "Authorization code" grant type is enabled in application
- Ensure application is active and not expired
4. IP Address Blocked¶
Error: 403 Forbidden - Network access not allowed
Solutions:
- Add your server's IP address to the application's IP whitelist
- Verify you're connecting from the whitelisted IP address
- Contact your network administrator to confirm your public IP
Getting Help¶
For additional support:
- Check the HouMeerOver API Documentation
- Verify browser network tab for detailed error responses
- Contact support with:
- Application name and client_id
- Complete error messages
- Steps to reproduce issue
Next: Explore API Endpoints to start using your authenticated access, or return to OAuth2 Overview for other authentication options.